A battery backup generator is a crucial tool for maintaining power during outages. It provides a reliable energy source when utility power fails. These generators can keep essential appliances running, ensuring comfort and safety in homes.
Understanding how a battery backup generator functions is vital. It typically stores energy in batteries, converting it into electricity during blackouts. When the grid goes down, the system activates automatically, supplying power immediately. Some models allow for manual operation as well.
However, not all battery backup generators are created equal. Their capacity varies, affecting the duration and number of devices they can support. Users often find themselves questioning their needs versus the generator's capabilities. Evaluating this can be challenging but is necessary for making informed choices.

A battery backup generator is a vital power solution. It provides electricity during outages. These systems store energy in batteries, allowing devices to run seamlessly. The main purpose is to ensure continuity in power supply. Many homes and businesses rely on these generators for critical operations.
According to industry reports, the demand for battery backup generators has increased by 20% annually. This growth stems from the rising frequency of power outages and natural disasters. During outages, a battery backup can provide power for hours. However, users often underestimate the batteries' capacity. This can lead to unexpected shutdowns of essential systems.
Battery backup generators are not flawless. They have limitations and require regular maintenance. Users must monitor battery health for optimal performance. Some systems take longer to recharge than anticipated. Proper installation is also crucial. A poorly installed unit could lead to power supply failures. Understanding these factors helps users make informed decisions.
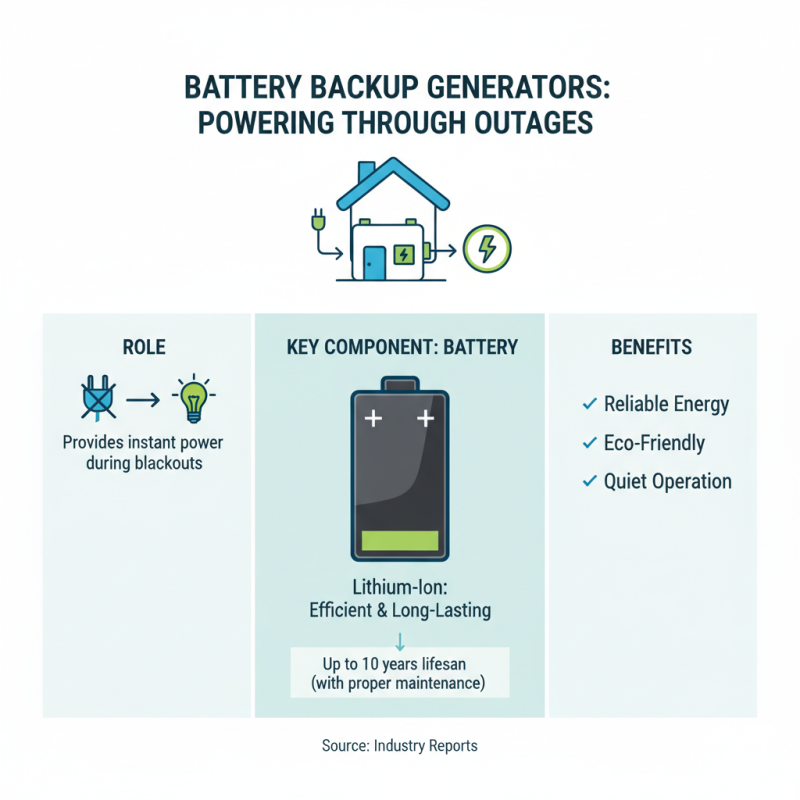
Battery backup generators play a crucial role in providing power during outages. Understanding their key components helps in recognizing their functionality. The main component is the battery itself, storing energy for later use. Most modern batteries are lithium-ion, known for efficiency and longevity. According to industry reports, these batteries can last up to 10 years if properly maintained.
Another vital part is the inverter. It converts stored DC power into AC power, suitable for household appliances. High-quality inverters ensure minimal energy loss during this conversion. Some systems come with automatic transfer switches. These switches detect power loss and activate the generator instantly, minimizing downtime. A report from a leading energy analyst notes that real-time switching technology improves reliability for 95% of users.
While these components provide solid performance, challenges remain. Batteries can degrade gradually, impacting energy storage capacity. Inverters can also malfunction, leading to power interruptions. Regular maintenance checks are necessary but often overlooked. Data from a recent usage study reveals that 30% of users neglect these checks, resulting in unexpected failures. Keeping systems updated is essential for ensuring reliability.
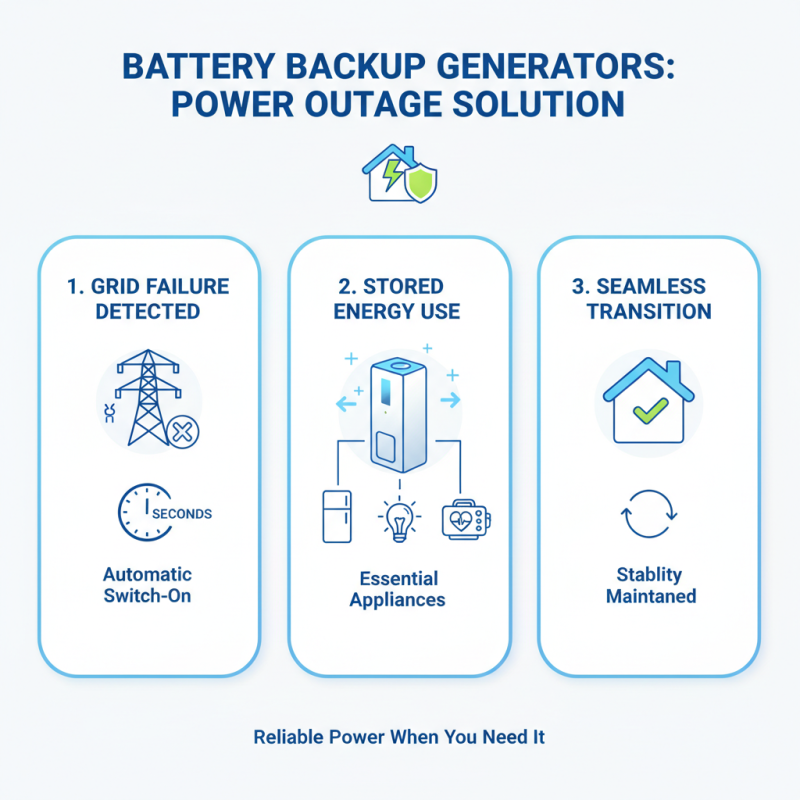
Battery backup generators serve a crucial role during power outages. When the grid fails, these devices automatically kick in. They use stored energy in batteries to power essential appliances. Lights, refrigerators, and medical equipment can stay operational. The generator senses the outage and switches on within seconds. This seamless transition helps maintain stability.
These systems rely on effective technology. Battery sizes vary, so plan according to your needs. Some models allow expansion for added capacity. Regular maintenance is important to ensure reliability. Check battery health often and replace old batteries as needed. Many users overlook this step and face issues during outages.
Noise can be another concern. While battery backup generators are quieter than traditional ones, they aren't silent. Consider locations to minimize disruption. Also, assess your power demands. Avoid overloading the system. Understanding your energy use helps optimize performance. A thoughtful approach ensures a smoother experience when the lights go out.
Battery backup generators are essential for maintaining power during outages. They provide a reliable source of electricity when the grid fails. Understanding their efficiency ratings is crucial for consumers. Efficiency is often determined by battery capacity and runtime.
Battery capacity refers to the amount of energy stored, usually measured in amp-hours. A higher capacity typically means the generator can run longer. However, increasing capacity can lead to increased weight and cost. Runtime is how long the generator can provide power. It's influenced by the load placed on it. There may be times when the generator runs out of power sooner than expected, especially with high-demand devices.
Considering these factors, users should assess their needs carefully. It's necessary to consider both the devices intended for use and the expected duration of an outage. Real-world applications may reveal challenges, such as managing expectations versus actual performance. Remember, no generator is perfect. Users often find they need more capacity after purchasing.
This chart illustrates the efficiency ratings of a battery backup generator focusing on three key dimensions: Battery Capacity in Amp-hours (Ah), Runtime in hours, and Efficiency percentage. The data represents a typical configuration that balances capacity and operational efficiency, indicating the generator's ability to sustain power during outages.
Battery backup generators and traditional generators serve the same fundamental purpose but with different technologies and applications. Battery backup generators use rechargeable batteries to store energy, providing immediate power during outages. They are quieter and emit no fumes, making them ideal for residential areas. In contrast, traditional generators typically run on gasoline or diesel. They generate noise and require proper ventilation due to exhaust emissions. According to industry reports, battery backups have seen a 20% growth rate in recent years, reflecting a shift towards cleaner energy.
The installation and maintenance of both systems differ significantly. Battery backup systems usually require less maintenance and have a more straightforward setup. However, their power output is limited compared to traditional generators. For instance, a standard battery generator might only provide essential power, while a traditional unit can supply more substantial loads. This can be a critical factor during extended outages, where larger appliances need power. Yet, battery systems offer a chance for energy storage, which is crucial as renewable sources gain popularity.
Cost is another significant factor. Battery backup systems may have higher upfront costs, but they can save money in the long run. They operate more efficiently, especially with fluctuating energy prices. Poor understanding of energy needs can lead to poor choices. Buyers should reflect on their power requirements carefully. A mismatch in capacity could result in insufficient power during emergencies, highlighting the importance of informed decision-making.